
Natural Ozempic Alternatives: Boosting GLP-1 with Diet and Lifestyle
Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?
Studies suggesting artery function benefits after olive oil consumption have measured ischemia-induced, as opposed to flow-mediated, dilation, and there is just not good evidence that that is actually an index of endothelial function, which is what predicts heart disease.
What about extra-virgin olive oil? This retains a fraction of the anti-inflammatory phytonutrients found in the olive fruit and doesn’t appear to induce the spike in inflammatory markers caused by regular olive oil. It may have more of a neutral effect, compared to butter, which exerted a noxious effect that lasted for up to six hours. In the largest prospective study ever to assess the relationship between olive oil consumption and cardiac events (like heart attacks), there was a suggestion that virgin olive oil may be better than regular olive oil, but neither was found to significantly reduce heart attack rates after controlling for healthy dietary behaviors, like vegetable intake, which tends to go hand-in-hand with olive oil intake in Mediterranean diet studies.
Some studies, though, have shown that even extra-virgin olive oil may impair endothelial function. Why then do some studies suggest people’s endothelial function improves on a Mediterranean diet, which is rich in olive oil? Perhaps because that diet is also rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, and walnuts. Dietary fruits and vegetables seem to provide some protection against the direct impairment of endothelial function produced by high-fat foods, including olive oil. Thus, health improvements may be in spite of, rather than because of, the oil. Simply adding some vegetables to a fatty meal may partially restore arterial functioning and blood flow.
We can think of extra-virgin olive oil a little like fruit juice: It has nutrients, but the calories are relatively empty compared to those from the whole fruit. (Olives are, after all, fruits.) Freshly squeezed olive juice already has less nutrition than the whole fruit, but then olive oil producers also throw away the olive wastewater, which contains the water-soluble nutrients. As a result, we end up getting just a small fraction of the nutrition of the whole fruit by the time extra-virgin olive oil is bottled. Refined olive oil (non-virgin) is even worse and, along with other vegetable oils, offers scant nutrition for their heavy caloric loads.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Okea / Thinkstock. This image has been modified.

Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?

Almonds are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial for facial wrinkles.

By losing 15 percent of their body weight, nearly 90 percent of those who’ve had type 2 diabetes for less than four years can achieve remission.

What happened when topical olive oil was pitted against an ibuprofen-type drug for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis?

There is another reason to avoid palm oil and question the authenticity of extra-virgin olive oil.

What are the three sources of the liver fat in fatty liver disease and how do you get rid of it?

Is butter—and other saturated fats—bad for you or not?

Oil pulling may help with tooth sensitivity, but the risk of inducing lipoid pneumonia outweighs the benefits.

Natural topical remedies for eczema, including licorice root gel, St. John’s Wort cream, and emollients such as coconut oil, mineral oil, and petroleum jelly, are put to the test.

Sprinkling vinegar on greens may augment their ability to improve endothelial function.

What happens inside the arteries going to the hearts and brains of those who add nuts or extra virgin olive oil to their diet?

Does extra virgin olive oil have the same adverse effect on arterial function as refined oils and animal fats?

What are the four problematic nutritional aspects of even plant-based Mediterranean diets?

Does just reducing one’s intake of meat, dairy, and eggs significantly reduce mortality?

Of all the components of a healthy Mediterranean diet, which are associated with a longer lifespan?

A randomized controlled trial found that a Mediterranean-type diet can dramatically lower the risk of subsequent heart attacks. How does it compare with plant-based diet data?

A randomized controlled trial found that a Mediterranean-type diet can dramatically lower the risk of subsequent heart attacks. How does it compare with plant-based diet data?

Not eating walnuts may double our risk of dying from heart disease (compared to at least one serving a week)—perhaps because nuts appear to improve endothelial function, allowing our arteries to better relax normally.

Just a few small servings of nuts a week may increase our lifespan and lower cancer risk.

To stay out of oxidative debt, we need to take in more antioxidants than we use up.

Some foods appear protective against the development of skin wrinkles—while others may make them worse.
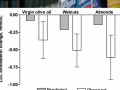
The short-term effect of replacing refined olive oil with extra virgin olive oil, walnuts, or almonds on cardiovascular risk factors.

Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory properties of white compared to yellow and purple potatoes. Purple potatoes may also help lower high blood pressure.