
One in a Thousand: Ending the Heart Disease Epidemic
Many of our most common diseases found to be rare, or even nonexistent, among populations eating plant-based diets.

Many of our most common diseases found to be rare, or even nonexistent, among populations eating plant-based diets.

Coronary heart disease, our #1 cause of death, was found to be almost non-existent in a population eating a diet centered around whole plant foods.

Those eating calorie-dense diets may have a reduced capacity to enjoy all of life’s pleasures by deadening dopamine pathways in the brain.

The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.

Phytonutrients in certain plant foods may block the toxic effects of industrial pollutants, like dioxins, through the Ah receptor system.

If doctors can eliminate some of our leading killers by treating the underlying causes of chronic disease better than nearly any other medical intervention, why don’t more doctors do it?

Americans eating meat-free diets average higher intakes of nearly every nutrient, while maintaining a lower body weight—perhaps due, in part, to their higher resting metabolic rates.

Might the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of plant-based diets undermine some of the benefits of exercise?

Too much choline—a compound concentrated in eggs and other animal products—can make bodily secretions smell like rotting fish, and may increase the risk of heart disease, due to conversion in the gut to trimethylamine.

The role white and pink (red) grapefruit may play in weight loss and cholesterol control, as well as the suppression of drug-clearance enzymes within the body.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.

Simple changes in diet and lifestyle may quadruple a woman’s survival rate from breast cancer.

Reducing the ratio of animal to plant protein in men’s diets may slow the progression of prostate cancer.

A plant-based diet may not only be the safest treatment for multiple sclerosis; it may also be the most effective.

By age 10, nearly all kids have fatty streaks in their arteries. This is the first sign of atherosclerosis, the leading cause of death in the United States. So the question for most of us is not whether we should eat healthy to prevent heart disease, but whether we want to reverse the heart disease we may already have.

Plant-based diets may prove to be a useful nutrition strategy in both cancer growth control as well as lifespan extension, because these diets are naturally lower in methionine.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.

A higher rate of cancer deaths among those that handle and process meat is attributed to infection with viruses, and chronic exposure to animal proteins.

Public health campaigns can use vanity to improve fruit and vegetable consumption, since experiments show carotenoid phytonutrients improve the physical attractiveness of African, Asian, and Caucasian faces.

Men eating pistachio nuts experienced a significant improvement in blood flow through the penis accompanied by significantly firmer erections in just three weeks—perhaps due to pistachios’ antioxidant, arginine, and phytosterol content.

Since both coronary heart disease and impotence can be reversed with a healthy diet, sexual dysfunction can be used as a motivator to change poor lifestyle habits.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.

Phytonutrients in citrus, such as hesperidin, may increase blood flow sufficient to warm the hands and feet of those with cold sensitivity.
Women suffering with dysmenorrhea who switch to a plant-based diet experience significant relief in menstrual pain intensity and duration.

Natural monoamine oxidase enzyme inhibitors in fruits and vegetables may help explain the improvement in mood associated with switching to a plant-based diet.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Cancer cells are commonly present in the body, but cannot grow into tumors without hooking up a blood supply. Angiogenesis inhibitors in plant foods may help prevent this from happening.
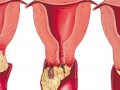
Most young women get infected with human papilloma virus, the cause of cervical cancer, but most are able to clear the infection before the virus causes cancer. What dietary changes can improve viral clearance?

About half of America’s trans fat intake now comes from animal products.
A more plant-based diet may help prevent vaginal infections, one of the most common gynecological problems of young women.

We’ve known our mental state can affect our gut flora, but might our good bacteria be affecting our mental state?

Modest lifestyle changes that include the avoidance of alcohol may cut the odds of breast cancer in half, but certain grapes appear to contain natural aromatase inhibitors that may undermine the ability of breast tumors to produce their own estrogen.
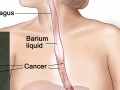
A randomized phase II clinical trial on the ability of strawberries to reverse the progression to esophageal cancer.

Nearly 5,000 breast cancer deaths a year may be attributable to just light drinking (up to one drink a day).

A tablespoon a day of ground flax seeds appears to improve ovarian function, and is considered a first-line therapy for breast pain associated with one’s period (cyclical mastalgia).
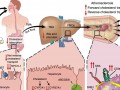
Expanding on the subject of my upcoming appearance on The Dr. Oz Show, a landmark new article in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that choline in eggs, poultry, dairy, and fish produces the same toxic TMAO as carnitine in red meat—which may help explain plant-based protection from heart disease and prostate cancer.
Plant-based diets appear to offer relief from a variety of menstrual symptoms, including cramping, bloating, and breast pain (cyclical mastalgia).
Two theories about the buildup of subcutaneous fat, involving the chemical spermine and the hormone adiponectin, suggest a plant-based diet may help with cellulite.

The story behind the first U.S. dietary recommendations report explains why, to this day, the decades of science supporting a more plant-based diet have yet to fully translate into public policy.

A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of flax seeds in breast cancer patients finds flax appears to have the potential to reduce tumor growth—in just a matter of weeks.