
Fasting for Post-Traumatic Brain Injury Headache
What effect do fasting and a plant-based diet have on TBI and migraines?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Dawn Handschuh
Arachidonic acid is an inflammatory omega-6 fatty acid. Our bodies produce this nutrient, and its excess may lead to inflammatory diseases and mood disorders.
Arachidonic acid is found in animal products, like poultry and eggs. The amount of arachidonic acid found in just one egg a day elevated arachidonic acid levels in the bloodstream, Japanese researchers learned.
Arachidonic acid may trigger brain inflammation. High blood levels have been associated with a greater risk of suicide and depressive episodes. On the other hand, diets high in carbohydrate and low in fat and protein (with little or no arachidonic acid) may be associated with lower levels of anxiety and depression, according to epidemiological studies.
In one study, overweight or diabetic employees who went on a whole food, plant-based diet reported increased energy, better sleep patterns and improved mental health compared to a control group given no diet restrictions. Their work productivity also showed improvement.
A similar subsequent study of employees at 10 corporate sites showed notable improvements in depression, anxiety and emotional well-being among those following a meat-free, plant-based diet.
Animal protein from meat and fish has also been associated with a higher risk of inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Arachidonic acid has been identified as one possible reason why. Even a semi-vegetarian diet has been shown to be highly beneficial in preventing relapses among patients suffering from Crohn’s disease.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

What effect do fasting and a plant-based diet have on TBI and migraines?

What happens when metastatic prostate cancer patients were taught to increase intake of whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and beans, and to decrease consumption of meat, dairy, and junk?

The aspirin compounds naturally found in plant foods may help explain the lower cancer rates among those eating plant-based diets.

In this “best-of” compilation of his last four year-in-review presentations, Dr. Greger explains what we can do about the #1 cause of death and disability: our diet.

What can we eat to combat “inflamm-aging,” the chronic low-grade inflammation that accompanies the aging process?

The most comprehensive controlled trial of diet and mood finds that a plant-based nutrition program in a workplace setting across ten corporate sites significantly improves depression, anxiety, and productivity.

Natural monoamine oxidase enzyme inhibitors in fruits and vegetables may help explain the improvement in mood associated with switching to a plant-based diet.

People eating conventional diets may ingest a trillion microparticles of the food-whitening additive, titanium dioxide, every day. What implication might this have for inflammation in the gut?

There are rare birth defects in which the inability to produce certain compounds requires an exogenous source. Presented here is a case report of a boy with a mutation in his carnitine transport system.

The egg industry is attempting to improve the fatty acid lipid profile of eggs by feeding blubber from the Canadian harp seal hunt to laying hens.
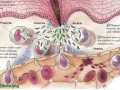
Chicken and eggs are the top sources of arachidonic acid in the diet—an omega-6 fatty acid involved in our body’s inflammatory response.

Arachidonic acid may play a role in cancer, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune disorders.
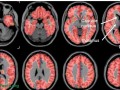
The purported role arachidonic acid plays in brain inflammation could explain why eliminating chicken, fish, and eggs may improve symptoms of mood disturbance, depression, anxiety, and stress within two weeks.