
How Much Does Meat Affect Longevity?
If you care about your health so much that it would be unthinkable to light up a cigarette before and after lunch, maybe you should order a bean burrito instead of a meaty one.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Selena
Red meat consumption has been associated with an increased risk of total mortality, cardiovascular disease mortality, and cancer mortality. On average, there are 64 times more antioxidants in plant foods than animal foods. The animal protein in meat may even have a pro-oxidant effect. Because food is a package deal, the nutrients in products such as beef cannot be obtained without cholesterol, saturated fat, and hormones. Red meat also contains carnitine, which can ultimately leads to the buildup of TMAO circulating throughout our bloodstream. TMAO increases the buildup of cholesterol in the inflammatory cells in the atherosclerotic plaques in our arteries, which is associated with a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, and death. Another risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and death is choline, found primarily in eggs, milk, fish, liver, poultry and red meat.
Meat appears to actually speed up the aging process by contributing to the loss of the telomere caps of our DNA and through the presence of AGEs (thought to likewise speed up the aging process). Vegetarians report less negative emotions than omnivores, possibly due to the inflammatory omega-6 arachidonic acid in meat. The sex steroid hormones in beef may affect the development of pregnant women’s son’s genitals in the womb. Meat intake has also been associated with women’s infertility and dementia. Tick-bite induced meat allergies may help explain idiopathic hives in children. Pancreatic cancer has been linked to intake of animal fat (including beef fat), though red meat is still better than poultry. Acute myeloid leukemia as well as other types of leukemia have been associated with meat intake.
In terms of fecal contamination, beef tends to be safer than chicken because the skin of cows is not eaten. Red meat is safer than white meat and fish in regards to flame retardant chemical contamination and safer than chicken and fish in terms of methionine amounts, which have been found to stimulate the growth of cancer cells. It is also poses a lower risk for prostate cancer than poultry, eggs, and refined grains, as well as a lower diabetes risk than fish (see also here) and 40% less weight gain than poultry. Red meat is riskier than white meat for colon cancer. PCBs are found in highest concentrations in fish and eggs, milk and milk products, and meat and meat products from land based animals, in that order. Finally, fast food burgers have been found to contain the following: blood vessels, nerves, cartilage, and only 2.1%-14.8% meat.
In September 2019, the Annals of Internal Medicine released a press release with the headline: “New guidelines: No need to reduce red or processed meat consumption for good health”. See Dr. David Katz’s response to these publications here.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Uwe Ruhrmann / Pixabay. This image has been modified.

If you care about your health so much that it would be unthinkable to light up a cigarette before and after lunch, maybe you should order a bean burrito instead of a meaty one.

Big Meat downplays the magnitude of meat mortality.

The meat industry’s own study concluded that meat consumption increased the risk of cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and premature death.

The same person paid by Big Sugar to downplay the risks of sugar was paid by Big Meat to downplay the risks of meat.

The meat industry comes up with a perversion of evidence-based medicine.

International Life Sciences Organization, a nonprofit, is accused of being a front group for Coca-Cola and other junk food giants.

Do nut eaters live longer simply because they swap in protein from plants in place of animal protein?

Switching to a plant-based diet has been shown to achieve far better outcomes than those reported on conventional treatments in both active and quiescent stages in both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.

Researchers tested 76 samples of different kinds of organic and conventional meats for 33 different carcinogens.

What are the eight preparation methods to reduce exposure to carcinogens in cooked meat?

The same diet that helps regulate hormones in women may also reduce exposure to endocrine-disrupting pollutants.

Do the medium-chain triglycerides in coconut oil and the fiber in flaked coconut counteract the negative effects on cholesterol and artery function?

What we eat determines what kind of bacteria we foster the growth of in our gut, which can increase or decrease our risk of some of our leading killer diseases.

Why does the leading cancer and diet authority recommend we avoid bacon, ham, hot dogs, sausage, and all other processed meats—including chicken and turkey?

Interventional studies support the population data that animal protein consumption appears to markedly increase the risk of kidney stones.

The negative impact of red meat on our cholesterol profile may be similar to that of white meat.
Studies on more than a thousand children suggest that a viral infection may play a role in childhood obesity by increasing both the number and size of fat cells.

Carcinogens in grilled and baked chicken may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, while curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, may sometimes help even in advanced stages of the disease.

Rural India has the lowest validated Alzheimer’s rates in the world. Is it due to the turmeric in their curry, or their largely plant-based diets?

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting-edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our leading causes of death and disability.
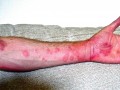
The rising incidence of tick-bite induced meat allergies may account for cases of previously unexplained (“idiopathic”) persistent hives among children.

The relationship between fish consumption and diabetes risk may be due to toxic pollutants that build up in the aquatic food chain.

Phytic acid (phytate), concentrated in food such as beans, whole grains, and nuts, may help explain lower cancer rates among plant-based populations.

How many months does it take to clear 99% of the mercury and other industrial toxins from one’s body, and what role might our fat stores play in holding on to fat-soluble pollutants?

Choline may be the reason egg consumption is associated with prostate cancer progression and death.

Too much choline—a compound concentrated in eggs and other animal products—can make bodily secretions smell like rotting fish, and may increase the risk of heart disease, due to conversion in the gut to trimethylamine.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.
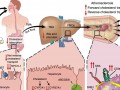
Expanding on the subject of my upcoming appearance on The Dr. Oz Show, a landmark new article in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that choline in eggs, poultry, dairy, and fish produces the same toxic TMAO as carnitine in red meat—which may help explain plant-based protection from heart disease and prostate cancer.

Other than pet food and fish (which may be most contaminated), how do fire-retardant chemicals (PBDEs) and polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) concentrate in the American food supply?
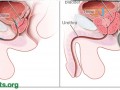
All men should consider eating a prostate-healthy diet, which includes legumes (beans, peas, lentils, soy); certain vegetables (like garlic and onions); certain seeds (flax seeds); and the avoidance of refined grains, eggs, and poultry.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.

In a study of a half million people, which was most associated with the risk of developing lymphoma? Red meat, processed meat, poultry, offal, eggs, or milk?

Monday, March 12, 2012: The Harvard Health Professionals Follow-up Study and the Harvard Nurses’ Health Study concluded that red meat consumption was associated with living a significantly shorter life—increased cancer mortality, increased heart disease mortality, and increased overall mortality.

Some herbs and spices—including cinnamon, cloves, lemon balm, marjoram, oregano, and peppermint—are so rich in antioxidants that just a small pinch can go a long way.

500 foods were tested for advanced glycation end products (AGEs).
The average “bad” cholesterol (LDL) level in people having heart attacks is in the “near-optimal” range, suggesting that the current guidelines are too lax.

The top three sources of industrial toxins in the diet are fish oil, fish, and eggs.

Eating chicken during pregnancy may affect the size and development of one’s son’s penis due to phthalate contamination of the meat.

On average, plant foods have 64 times more antioxidant power than red meat, poultry, fish, dairy, and eggs— but is it a fair comparison?