Wrinkles
The skin is the fastest-growing and largest organ in our body—about 20 square feet, accounting for about 10 percent of our body weight. It acts as the most conspicuous mirror of the aging process. As our skin becomes thinner, it is more easily damaged, loses volume and elasticity, and can sag and wrinkle.
The three main constituents that make up the bulk of our skin are collagen, hyaluronic acid, and elastin. Collagen, which makes up about 75 percent, contributes strength and firmness, hyaluronic acid maintains moisture in the skin by trapping water, and stretchy elastic fibers containing elastin make up about 1 to 2 percent of our skin and help it bounce back into shape.
Wrinkles occur where fault lines develop in aging skin, a process comparable to breaking in leather gloves. Over time, the skin folding caused by everyday facial expressions etches the temporary grooves into permanent wrinkles. The key to preventing wrinkles is preventing the underlying structural damage that makes your skin susceptible to them via choices such as tobacco avoidance and regular sun protection.
Indeed, protecting our skin from sun damage is the single most effective way to slow the signs of aging. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), chemicals in air pollution that appear to contribute to skin aging, can also be found in foods like meat. The carotenoid nutrients in certain colorful fruits and vegetables can offer a more “glowing” appearance, and the nutrients in greens may improve skin elasticity, collagen status, and facial wrinkles. Drinking extra water can decrease symptoms of skin dryness and roughness; honeybush tea may reduce eye wrinkles; cocoa powder may increase skin thickness and elasticity and decrease wrinkle severity; ground flaxseeds can improve skin smoothness; and soy foods can improve facial skin elasticity and fine wrinkles. Indeed, a whole food, plant-based diet can be considered an anti-wrinkle diet, but a regular, reliable source of vitamin B12 is critical.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Image by Peggychoucair from Pixabay. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Wrinkles


How to Naturally Reduce Wrinkles with Food
Almonds are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial for facial wrinkles.
What Causes Wrinkles?
Over time, the skin folding caused by everyday facial expressions etches once-temporary grooves into permanent...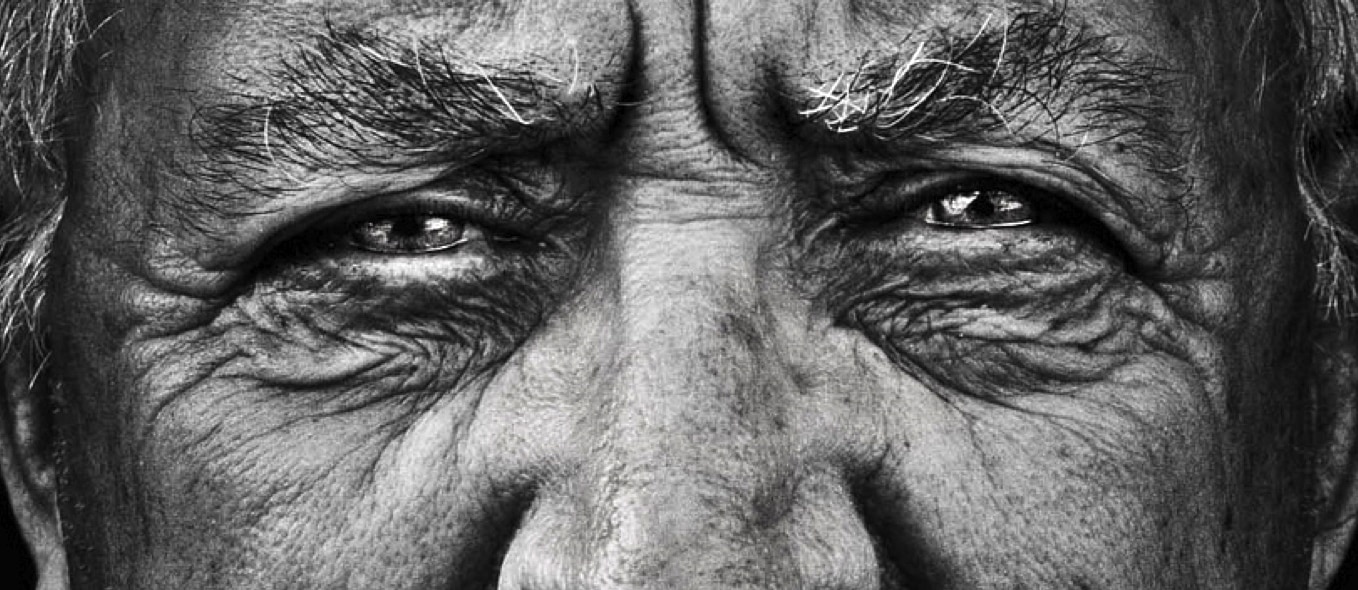
Beauty Is More than Skin Deep
Some foods appear protective against the development of skin wrinkles—while others may make them worse.All Videos for Wrinkles
-

Choosing the Safest and Most Effective Sunscreen (webinar recording)
Has sunscreen been proven to prevent skin aging and cancer?
-

The Best Foods for Your Skin
Greens, apples, tomato paste, and grapes are put to the test as edible skin care candidates.
-
How to Prevent Wrinkles with Diet
The evidence supports the recommendation to follow a whole food, plant-based diet for healthier looking skin.
-

The Best Type of Sunscreen to Use
The FDA has concluded that only two sunscreen ingredients can be considered safe: zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
-

Does Sunscreen Cause or Prevent Skin Cancer?
Sunscreen is put to the test in a randomized controlled trial to see if it can actually prevent skin cancer.
-

The Single Most Important Thing for Anti-Aging Skin Care
Sunscreen is put to the test in a randomized controlled trial to see if it can actually slow skin aging.
-

How to Boost Collagen Synthesis with Diet
Which foods can increase collagen deposition and prevent wrinkles?
-

Do Collagen Supplements Work for Skin Aging?
I assumed that collagen proteins would get completely broken down in the digestive tract, but I was wrong.
-

What Causes Wrinkles?
Over time, the skin folding caused by everyday facial expressions etches once-temporary grooves into permanent wrinkles, but only in the context of underlying structural damage.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Fillers, Chemical Peels, and Laser Skin Resurfacing
Chemical peels and laser skin resurfacing may do more harm than good, and filler injections in certain areas of the face can cause blindness in rare cases.
-
The Efficacy, Safety, and Side Effects of Botox and Facelifts
Botox injections and facelift surgery are considered to be relatively safe with complications happening in only about 1 in 2,000 and 1 in 20 procedures, respectively.
-

The Benefits of Topical Vitamin C for Reversing Skin Aging
What are the pros and cons of alpha hydroxy acid lotions and chemical peels, as well as the roles of topical antioxidants vitamin E and C, in reversing the signs of aging?
-
The Benefits of Topical Niacinamide for Reversing Skin Aging
Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3 also known as nicotinamide, is a precursor to two potent antioxidants that can help reverse signs of skin aging.
-

Topical Retinoids to Reverse Skin Aging
Tretinoin, also known as all-trans retinoic acid (sold under a variety of brands including Retin-A), can reverse the signs of aging, but at what cost?
-

What Is the Most Important Anti-Aging Cream Ingredient?
Most anti-aging creams may work no better than typical moisturizers.
-

How Not To Age – Live Presentation
In this live lecture, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his latest book, How Not to Age, a New York Times Best Seller.
-

How to Naturally Reduce Wrinkles with Food
Almonds are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial for facial wrinkles.
-

The Best Way to Get Vitamin D: Sun, Supplements, or Salons?
If one is going to make an evolutionary argument for what a “natural” vitamin D level may be, how about getting vitamin D in the way nature intended—that is, from the sun instead of supplements?
-

How to Slow Brain Aging by Two Years
The consumption of blueberries and strawberries is associated with delayed cognitive aging by as much as 2.5 years—thought to be because of brain-localizing anthocyanin phytonutrients, as shown on functional MRI scans.
-

Preventing Wrinkles with Diet
What dietary intervention may significantly protect against wrinkles in the crow’s foot area around the eyes?
-

Beauty Is More than Skin Deep
Some foods appear protective against the development of skin wrinkles—while others may make them worse.
-

Glycotoxins
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in our diet are thought to accelerate the aging process.
