
Food Poisoning: Causes and Prevention
Why do contaminated poultry products cause the most foodborne deaths?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Eric
E. coli exposure may lead to health problems such as irritable bowel syndrome and urinary tract infections caused by contaminated chicken. But cranberry juice may help prevent bladder infections. Turkey meat may also contain dangerous amounts of the E. coli bacteria. Meat glue, an enzyme used to hold different pieces of meat together, might harbor E. coli bacteria. Handling money could also result in E. coli exposure due to bacteria fecal contamination. Those undergoing chemotherapy should be cautious of eating potentially E. Coli contaminated foods such as undercooked eggs, meat, dairy, and sprouts.
The potentially deadly toxin produced by E. coli O157:H7, which can shut down the kidneys of children, attaches to Neu5Gc, a foreign meat molecule that may contribute to the progression of cancer and heart disease.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Why do contaminated poultry products cause the most foodborne deaths?

Why can a single meal high in saturated fat impair cognition?
Tainted chicken may result in more than a million urinary tract infections in American women every year.

Emulsifiers are the most widely used food additive. What are they doing to our gut microbiome?

What are the direct health implications of making clean meat—that is, meat without animals?

We need to reform the food system before it’s too late.

Endotoxins can build up on pre-chopped vegetables and undermine some of their benefits.
Comparing contamination rates for antibiotic-resistant E. coli and ExPEC bacteria that cause urinary tract infections

Can UTI-causing ExPEC E. coli bacteria be transferred human-to-human from those who eat chicken?

What’s the best household cleaning product to use?
Green tea may help with athlete’s foot, dental plaque, acne, impetigo, and bladder infections, but if it’s so good at killing bacteria, what may it do to our gut flora?

In this “best-of” compilation of his last four year-in-review presentations, Dr. Greger explains what we can do about the #1 cause of death and disability: our diet.

Immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, are often denied fresh fruits and vegetables to ostensibly protect them against foodborne illness.

Used in about eight million pounds of meat every year in the United States, the “meat glue” enzyme, transglutaminase, has potential food safety and allergy implications.

Chronic red pepper powder ingestion may be an effective treatment for IBS and chronic dyspepsia (indigestion), both of which can arise from food poisoning.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.
Cranberries may reduce the recurrence of urinary tract infections, but their role in treating infections is limited.

Handling chicken can lead to the colonization of one’s colon with antibiotic-resistant E. coli that may result in bladder infections in women.
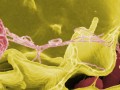
Hundreds of thousands of Americans are Salmonella-poisoned by poultry every year—yet it remains legal to sell meat proven to be contaminated.

Those who eat meat risk food poisoning from undercooked meat, but also exposure to cooked meat carcinogens in well-cooked meat. By boiling meat, non-vegetarians can mediate their risk of both.
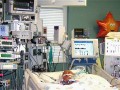
The foreign meat molecule Neu5Gc may not only contribute to the progression of cancer and heart disease by supplying inflammation, but may also set children up for life-threatening reactions to E. coli toxins originating in the same animal products.

A profile of the study “Dirty Money: An Investigation into the Hygiene Status of Some of the World’s Currencies as Obtained from Food Outlets.” The level of fecal bacteria contamination on banknotes is compared between Australia, Burkina Faso (Africa), China, Ireland, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nigeria, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and the United States.

An investigation finds 47% of U.S. retail meat tested is contaminated with staph (Staphylococcus) bacteria. Turkey appears most likely to harbor contagion.

How contaminated is the American meat supply with fecal matter?

Fecal bacteria may contaminate alfalfa seed sprouts and present a food safety risk.