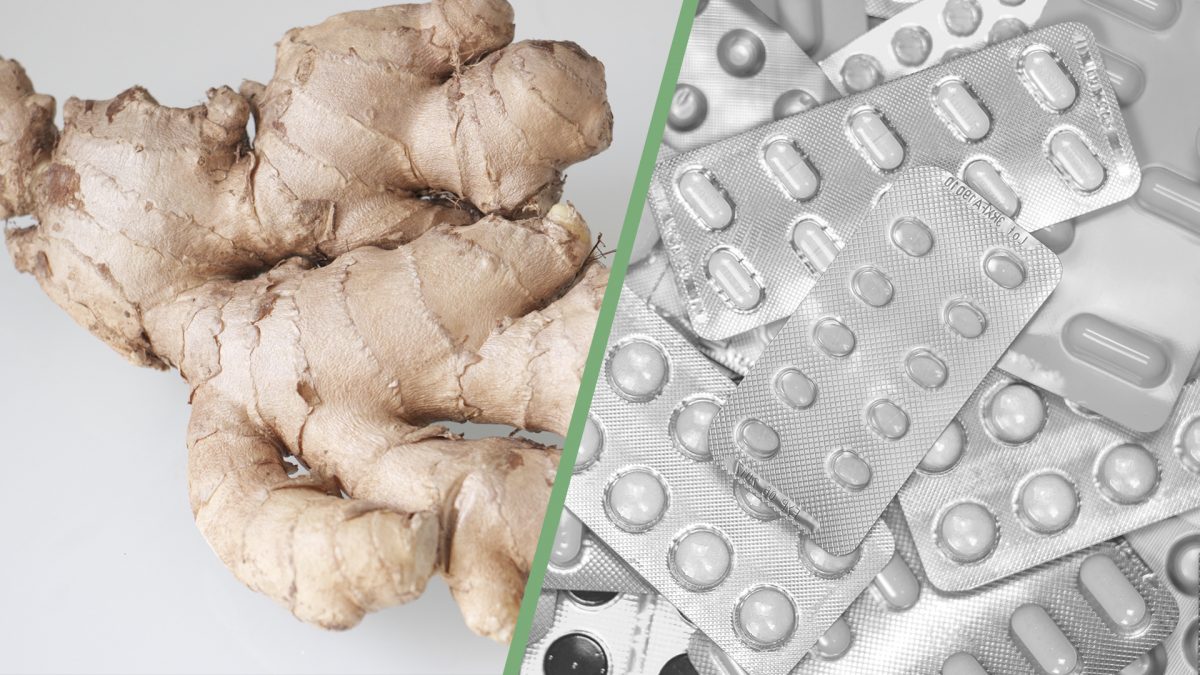
Ginger
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Randy
Ginger has been used for thousands of years in traditional healing systems. In India, it’s known as maha-aushadhi, meaning “the great medicine.”
Beating out Dramamine in a head-to-head test, it’s considered to be a nontoxic, broad-spectrum antiemetic (antivomiting agent) effective in countering nausea during motion sickness, pregnancy, chemotherapy, radiation, and after surgery.
It has also been found to be useful for headaches, including migraines. A double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial compared its efficacy for the treatment of migraine headaches to sumatriptan (Imitrex), one of the top-selling, billion-dollar drugs in the world. Just one-eighth of a teaspoon of powdered ginger worked just as well and just as fast as the drug (and costs less than a penny). Most migraine sufferers started with moderate or severe pain, but after taking the drug or the ginger, ended up in mild pain or were entirely pain-free. The same proportion of migraine sufferers reported satisfaction with the results either way.
At least eight randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trials have been conducted on ginger for pain—everything from osteoarthritis, to irritable bowel, to painful periods. Overall, ginger extracts, like the powdered ginger spice you’d get at any grocery store, were found to be “clinically effective [pain-reducing] agents [with] a better safety profile than [the] drugs.” In some of the studies, it worked better than in others, which is thought to be due, in part, to the different doses that were used, as there’s a “strong dose-effect relationship.” The best results, in terms of reduction of pain, were with one-and-a-half or two grams a day, which is a full teaspoon of ground ginger.
Ginger is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but the maximum recommended daily dose of fresh ginger while pregnant is 20 grams (about four teaspoons of freshly grated gingerroot). Any more may have uterus-stimulating effects.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Pixabay. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Ginger


Benefits of Ginger for Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease
Ground ginger powder is put to the test for weight loss and NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty...
Ground Ginger to Reduce Muscle Pain
There have been at least eight randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of ginger for pain.
Benefits of Ginger for Menstrual Cramps
An eighth of a teaspoon of ground ginger power is tested head-to-head against the leading...
Ginger for Osteoarthritis
A quarter- to a half-teaspoon a day of powdered ginger can be as pain-relieving as...
Ginger for Nausea, Menstrual Cramps, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Powdered ginger can be a highly effective, cheap, easy-to-use, safer treatment for nausea, migraine headaches,...
Ginger for Migraines
An eighth teaspoon of powdered ginger was found to work as well as the migraine...All Videos for Ginger
-

Natural Ozempic Alternatives: Boosting GLP-1 with Diet and Lifestyle
Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?
-

How Not To Age – Live Presentation
In this live lecture, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his latest book, How Not to Age, a New York Times Best Seller.
-

Caffeine Shampoo and Rosemary Oil for Hair Growth
I cover natural topical treatments for hair growth, including pumpkin seed oil, caffeine, green tea, pyrithione zinc, ginger, Chinese knotweed, and rosemary.
-

The Best Diet for Fibromyalgia and Other Chronic Pain Relief
Anti-inflammatory diets can be effective in alleviating chronic pain syndromes.
-

Fenugreek Benefits for Sexual Function, Painful Periods, and Milk Production
The hormonal benefits of fenugreek extend beyond the muscle-bulking testosterone boost.
-

Which Foods Are Anti-Inflammatory?
Foods that reduce inflammation. What does an anti-inflammatory diet look like?
-

Foods That Help Headache and Migraine Relief
Plant-based diets are put to the test for treating migraine headaches.
-

Evidence-Based Weight Loss – Live Presentation
In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.
-

Is Ginger Beneficial in a Diabetic Diet?
Ground ginger and ginger tea are put to the test for blood sugar control.
-

Benefits of Ginger for Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease
Ground ginger powder is put to the test for weight loss and NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
-

Ground Ginger to Reduce Muscle Pain
There have been at least eight randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of ginger for pain.
-

Benefits of Ginger for Menstrual Cramps
An eighth of a teaspoon of ground ginger power is tested head-to-head against the leading drug for the alleviation of painful periods.
-

Benefits of Marjoram for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Even a small amount of fresh herbs can double or even quadruple the antioxidant power of a meal. The abilities of oregano to decrease chromosomal damage from radiation and marjoram to affect hormone levels in women with PCOS are put to the test.
-

Ginger for Osteoarthritis
A quarter- to a half-teaspoon a day of powdered ginger can be as pain-relieving as ibuprofen, without the risk of damage to the intestinal lining.
-

Ginger for Nausea, Menstrual Cramps, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Powdered ginger can be a highly effective, cheap, easy-to-use, safer treatment for nausea, migraine headaches, and menstrual blood loss and pain. Does it also work for IBS intestinal cramping?
-

Natural Treatments for Morning Sickness
Can cannabis and ginger be considered safe and effective treatments for hyperemesis gravidarum (severe morning sickness during pregnancy)?
-

Fennel Seeds for Menstrual Cramps and PMS
Fennel seeds can work as effectively as drugs like ibuprofen for painful periods, and an eighth of a teaspoon of ginger powder three times a day can cut menstrual bleeding in half.
-

Boosting Brown Fat Through Diet
The fat-burning properties of brown adipose tissue can be boosted by cold exposure, certain flavor molecules, and arginine-rich foods.
-

Ginger for Migraines
An eighth teaspoon of powdered ginger was found to work as well as the migraine headache drug sumatriptan (Imitrex) without the side effects.
-

Peppermint Aromatherapy for Nausea
Is the relief of nausea and vomiting after surgery from sniffing peppermint extract due to the mint, the alcohol vapors, or just the controlled breathing?
-

Turmeric Curcumin and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Randomized controlled trial comparing the safety and efficacy of drugs versus curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, for the treatment of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Spicing Up DNA Protection
The DNA of those cooking with spices such as ginger, rosemary, and turmeric appears less susceptible to breakage.
-

Which Spices Fight Inflammation?
An elegant experiment is described in which the blood of those eating different types of spices—such as cloves, ginger, rosemary, and turmeric—is tested for anti-inflammatory capacity.
-

Reducing Radiation Damage with Ginger & Lemon Balm
A component of cooked ginger root protects human white blood cells in vitro against radiation-induced genetic damage, and lemon balm tea appears to protect radiology staff against radiation-induced oxidative stress.
-

Plants vs. Pesticides
Phytonutrients found in certain foods may protect against the toxic effects of industrial pollutants such as dioxin and DDT, suggesting a dual role for plant-based diets to reduce both exposure and subsequent damage.
-

Treating Gorlin Syndrome with Green Tea
Gorlin Syndrome, also known as basal cell nevus syndrome, is a rare genetic condition in which one’s body becomes covered in skin cancers. An astounding case is reported of a woman suffering from the syndrome, whose cancer progression was apparently reversed with topical green tea body wraps.
-

Dangerous Advice from Health Food Store Employees
Employees in natural food stores have been caught giving advice that is not only scientifically baseless, but also risky and downright dangerous.
-
Amyloid & Apple Juice
Ginger and apple juice appear to protect human nerve cells from the neurotoxic Alzheimer’s plaque protein amyloid beta in a petri dish.
