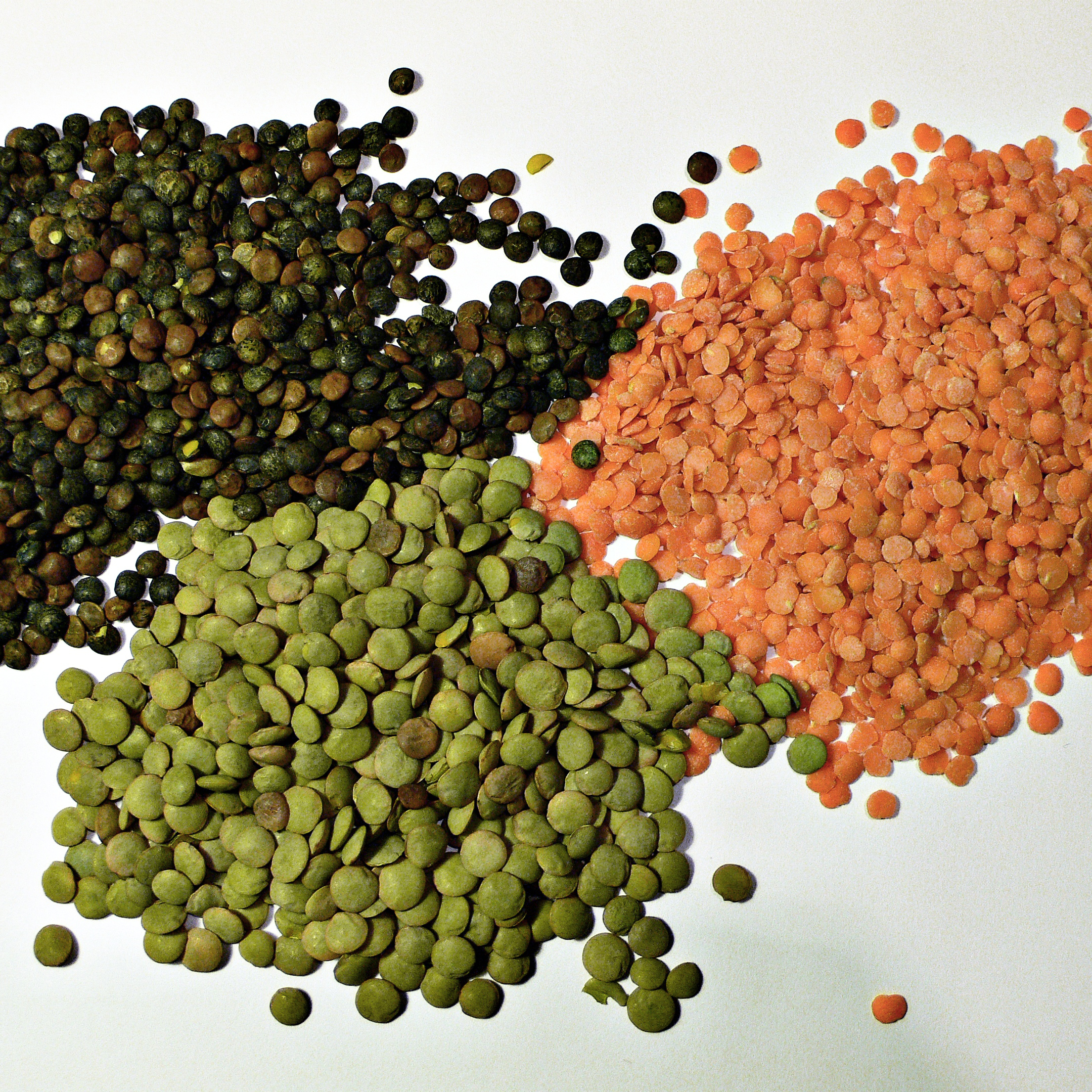
Lentils
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Linda
Lentils have the second-highest antioxidant content (behind black beans) among all tested legumes and offer significant levels of protein, iron, zinc, and folate. A diet rich in legumes may help reduce cholesterol, hypertension, and the risk of prediabetes, fibrocystic breast disease, and prostate cancer proliferation. They may offer significant anti-inflammatory effects, as well.
They are high in phytates, which may reduce the risk of colon cancer and may have protective effects against osteoporosis. Lentils and chickpeas appear to improve glycemic control (i.e., moderate blood sugar levels) not just at the meal when they are consumed, but even hours later or the next day. Lentils and other foods containing resistant starch may help block the accumulation in the colon of hydrogen sulfide, which is associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
Sprouted lentils have twice the antioxidant content as unsprouted, and red lentils beat other types in overall nutritive benefits.
Legumes’ reputation for flatulence production may be undeserved: studies show that intestinal gas issues appear to return to normal levels after a few days or weeks of increased legume intake.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Lentils


Benefits of Lentils and Chickpeas
Lentils and chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are put to the test.All Videos for Lentils
-

The Highest Antioxidant: Apple, Bean, Berry, Lentil, or Nut?
The best apple, bean, berry, lentil, and nut are the ones you’ll eat the most of; but if you don’t have a strong preference, which has the highest antioxidant power?
-

The Supplement Shown to Slow Age-Related Hearing Loss
Some studies found that higher levels of folate in the blood seem to correlate with better hearing, so researchers decided to put it to the test.
-

Greens, Green Tea, and Nuts Put to the Test for Telomeres
Not all plant foods are linked to less cellular aging based on telomere attrition, and not all animal foods are linked to more.
-

The Best Time to Exercise for Weight Loss
Burn off significantly more body fat exercising before meals, rather than after them.
-

Plant-Based Pregnancy Outcomes and Breast Milk
The composition of breast milk is compared between vegetarian and nonvegetarian women.
-

Strategies to Eat Less Meat
What is the most effective way to help people reduce their meat consumption?
-

Is Oatmeal Good for People with Diabetes?
Before there was insulin, there was the “oatmeal cure.”
-

The Impacts of Plant-Based Diets on Breast Cancer and Prostate Cancer
Why do people who eat more plants get less breast and prostate cancer?
-

The Best Diet for Fibromyalgia and Other Chronic Pain Relief
Anti-inflammatory diets can be effective in alleviating chronic pain syndromes.
-

The Harms Associated with Eating More Southern-Style Food
Diet appears to mediate the majority of the racial health gap.
-

Diet and Lifestyle for Cancer Prevention and Survival
What kind of diet should cancer patients eat?
-

Vitamin D May Explain Higher Bone Fracture Risk in Vegans
A combination of low calcium intake and low vitamin D exposure may explain higher bone fracture rates in British vegans.
-

How Much Does Meat Affect Longevity?
If you care about your health so much that it would be unthinkable to light up a cigarette before and after lunch, maybe you should order a bean burrito instead of a meaty one.
-

Are the Health Benefits of Nuts Limited to Those Eating Bad Diets?
Do nut eaters live longer simply because they swap in protein from plants in place of animal protein?
-

Blocking the Cancer Metastasis Enzyme MMP-9 with Beans and Chickpeas
Which legumes are best at inhibiting the matrix metalloproteinase enzymes that allow cancer to become invasive?
-

IARC: Processed Meat Like Bacon Causes Cancer
How did the meat industry, government, and cancer organizations respond to the confirmation that processed meat, like bacon, ham, hot dogs, and lunch meat, causes cancer?
-

How to Boost FGF21 with Diet for Longevity
Fasting and exercise can boost the longevity hormone FGF21, but what can we eat—or avoid eating—to get similar effects?
-

Glycemic Index of Potatoes: Why You Should Chill and Reheat Them
If you eat potatoes when they’re cold, as in potato salad, or chilled and reheated, you can get a nearly 40 percent lower glycemic impact.
-

How to Heal a Leaky Gut with Diet
The recommended diet for leaky gut treatment. Which foods and food components can boost the integrity of our intestinal barrier?
-

Plant-Based Eating Score Put to the Test
How can you get a perfect diet score?
-

The Best Diet for Crohn’s Disease Treatment
Switching to a plant-based diet has been shown to achieve far better outcomes than those reported on conventional treatments in both active and quiescent stages in both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
-

The Best Diet for Fatty Liver Disease Treatment
What are the three sources of the liver fat in fatty liver disease and how do you get rid of it?
-

The Benefits of Millet for Diabetes
What were the remarkable results of a crossover study randomizing hundreds of people with diabetes to one and a third cup of millet every day?
-

Dr. Greger in the Kitchen: Cran-Chocolate Pomegranate BROL Bowl
Prebiotic goodness for breakfast to keep your microbiome happy all day long.
-

Plant-Based Meat Substitutes Put to the Test
What are the effects of plant-based meats on premature puberty, childhood obesity, and hip fracture risk?
-

Plant-Based Protein: Are Pea and Soy Protein Isolates Harmful?
What are the different impacts of plant protein versus animal protein, and do the benefits of plant proteins translate to plant protein isolates?
-

Which Foods Have the Lowest Carbon Footprint?
How much greenhouse gas does the production of different foods cause measured in miles driven or lightbulb hour equivalents?
-

Win-Win Dietary Solutions to the Climate Crisis
The EAT-Lancet Commission lays out the best diet for human and planetary health.
-

Type 1 Diabetes Treatment: A Plant-Based Diet
Is it possible to reverse type 1 diabetes if caught early enough?
-

Do Vegetarians Really Have Higher Stroke Risk?
The first study in history on the incidence of stroke of vegetarians and vegans suggests they may be at higher risk.
-

The Immune System and COVID-19 Treatment
Are there immune-boosting foods we should be eating?
-
Fasting to Naturally Reverse High Blood Pressure
A whole food plant-based diet can be used to help lock in the benefits of fasting to kickstart the reversal of high blood pressure.
-

Evidence-Based Weight Loss – Live Presentation
In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.
-

Is Keto an Effective Cancer-Fighting Diet?
The clinical use of ketogenic diets for epilepsy and cancer: what does the science say?
-

Best Foods for Colon Cancer Prevention
A low-fiber diet is a key driver of microbiome depletion, the disappearance of diversity in our good gut flora.
-
How to Prevent Toxoplasmosis
The risk of contracting the brain parasite toxoplasma from kitty litter vs. meat.
-

The Orthorexia Nervosa Test
See how you score on the orthorexia “diagnostic” test.
-

The Best Diet for Diabetes
The case for using a plant-based diet to reduce the burden of diabetes has never been stronger.
-

Dairy and Cancer
How do we explain the increased risk of prostate cancer but the decreased risk of colon cancer associated with dairy consumption?
-
How to Treat Periodontitis with Diet
Plant-based diets are put to the test in the treatment of periodontal disease.
