
Do Men Who Have More Sex Live Longer?
When done right, love may protect your lover’s life.

When done right, love may protect your lover’s life.

What we eat determines what kind of bacteria we foster the growth of in our gut, which can increase or decrease our risk of some of our leading killer diseases.

Within 40 minutes of green tea consumption, we get a boost in antioxidant power in our bloodstream, and, within 60 minutes, an upregulation of DNA repair.

What role do soy phytoestrogens play in the prevention and treatment of breast cancer?
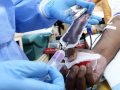
An extraordinary thing happened when those at high risk for heart disease were randomized to give blood—and it had nothing to do with their heart.

What are the protective components of dietary patterns and foods associated with lower risk of cerebrovascular disease, or stroke?

What happened to women who were randomized to eat more meat and dairy during pregnancy? What effect does animal protein consumption have on cortisol and testosterone levels in men?

The current generation of American kids may be one of the first generations to be less healthy and have shorter lifespans than their parents.

One third of men in their 30s may already have tiny, cancerous tumors in their prostates. How much tea would we have to drink to build up cancer-suppressing levels in our prostate tissue?

How the egg industry funded a study designed to cover up the toxic trimethylamine oxide reaction to egg consumption.

Should the active ingredient in aspirin be considered an essential vitamin?

Can the consumption of sesame seeds improve the clinical signs and symptoms of arthritis?
Given that diet is the number-one cause of death and disability, nutrition is surely the number-one subject taught in medical school, right? And it’s certainly the number-one issue your doctor talks with you about, right? If only. How can there be such a disconnect between the available evidence and the practice of medicine?

We have tremendous power over our health destiny and longevity.

Sun exposure is associated with lower rates of 15 different cancers and improved cancer survival. What happened when vitamin D supplements were put to the test?

How might we prevent and reverse hypertension, the number-one risk factor for death in the world?

As many as 37 percent of human breast cancer cases may be attributable to exposure to bovine leukemia virus.

Type 2 diabetes can be prevented, arrested, and even reversed with a healthy enough diet.

The majority of U.S. dairy herds are infected with a cancer-causing virus, but until recently, human testing for exposure was not sufficiently sensitive.

What happens when we put cancer on a plant-based diet?

Lifestyle approaches aren’t only safer and cheaper—they can work better, because they let us treat the actual cause of the disease.

What is the evidence that all pregnant women should follow the American Thyroid Association’s recommendation to take a daily iodine supplement?

What is the optimal source and amount of protein for senior citizens?

Only about 1 in 10,000 people live to be 100 years old. What’s their secret?

What can our nutrient requirements, metabolism, and physiology tell us about what we should be eating?

Despite less education on average, a higher poverty rate, and more limited access to health care, U.S. Hispanics tend to live the longest. Why?

How extreme was Dr. Kempner’s rice diet compared to traditional surgical approaches? Is there a safer alternative?
We don’t have to choose between the lesser of two evils: skin cancer versus internal cancers from vitamin D deficiency.

Why do some recommend thousands of units of supplemental vitamin D when the Institute of Medicine set the recommended daily intake at just 600 to 800 units?

The safe dose of vitamin D supplementation to get most of the population to the optimal level is 2,000 IU a day, but the elderly and overweight may need more.

What do 56 randomized clinical trials involving nearly 100,000 people between the ages of 18 and 107 show vitamin D can do to our lifespan?
Those with higher vitamin D levels tend to have lower rates of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, but is it cause and effect? Interventional trials finally put vitamin D to the test.

Why has fish consumption been associated with cognitive impairment and loss of executive function?

Our physiology evolved for millions of years eating a plant-based diet. What would happen if researchers tried to recreate our ancestral diet in the lab?
Avoid sugary and cholesterol-laden foods to reduce the risk of our most common cause of chronic liver disease.

A cup a day of beans, chickpeas, or lentils for three months may slow resting heart rate as much as exercising for 50 hours on a treadmill.

To maximize our lifespan, the target resting heart rate may be one beat a second or less.

The reason greens are associated with a significantly longer lifespan may be because, like caloric restriction, they improve our energy efficiency.

What was the meat industry’s response to the recommendation by leading cancer charities to stop eating processed meats, such as bacon, ham, hot dogs, sausage, and lunchmeat?

What three things can we do to lower our sodium intake? Are there any tricks for interpreting nutrition facts labeling on processed foods?