
IARC: Processed Meat Like Bacon Causes Cancer
How did the meat industry, government, and cancer organizations respond to the confirmation that processed meat, like bacon, ham, hot dogs, and lunch meat, causes cancer?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Randy
While animal protein intake is generally associated with weight gain, poultry such as turkey appears to be the worst, associated with 40% more weight gain than red meat or processed meat. When it comes to turkey, however, gaining a few extra pounds isn’t the only concern; with a high fat content, poultry appears to promote diabetes and the development of pancreatic cancer more than other animal products, potentially raising one’s risk of pancreatic cancer by 72% for every 50g increase in daily poultry consumption. Turkey consumption may also cause the rapid uptake and accumulation of the neurotoxin harman – linked to essential tremor, cancer, and Parkinson’s disease.
Turkey meat may contain toxic chemicals and life-threatening bacteria. Processed turkey meat appears to come pre-packaged with cancer causing agents, containing dangerously high levels of nitrosamines – the chemical compounds considered to be the most carcinogenic agents in cigarette smoke. Workers in poultry slaughtering and processing plants have significantly increased risk of dying from certain cancers including those of the cervix, penis, liver and pancreas, a phenomenon that might be explained by the increasing presence of cancer-causing viruses in poultry products. Men who regularly consume poultry have four times greater risk of developing prostate cancer compared with non-poultry eaters.
Turkey feed often contains antibiotics, which may foster the growth of multidrug resistant pathogens, including E. coli and Salmonella, which causes more deaths and hospitalizations than any other food borne illness. A 2011 study found that 47% of American retail meat tested was infected with Staphylococcus bacteria, with the bacteria present in 77% of turkey samples. Turkey was also found to have the highest amounts of flame retardant chemical pollutants. Most poultry, including turkey, is injected with phosphorous preservatives, which appear to increase the growth of food poisoning Campylobacter bacteria, damage blood vessels, accelerate aging, contribute to osteoporosis, and function as an arterial toxin. Furthermore, many birds are fed arsenic-containing drugs that are apparently converted by cooking into carcinogenic inorganic arsenic compounds, the harmful effects of which are magnified by feeding poultry the leftover guts, heads, feet, manure and feathers of other slaughtered birds, which are often laden with arsenic, in turn leading to increased arsenic exposure in humans who eat the meat. Sliced turkey has also been found to be contaminated with the dangerous chemical BPA, found in plastics, which has been linked to diabetes, erectile dysfunction, and our nation’s number one killer, cardiovascular disease.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Tim Sackton / Flickr. This image has been modified.

How did the meat industry, government, and cancer organizations respond to the confirmation that processed meat, like bacon, ham, hot dogs, and lunch meat, causes cancer?

What are the different impacts of plant protein versus animal protein, and do the benefits of plant proteins translate to plant protein isolates?

In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.
Comparing contamination rates for antibiotic-resistant E. coli and ExPEC bacteria that cause urinary tract infections

After the trans fat oil ban, the only remaining major sources of trans fat will be from meat and dairy.

Dietary guidelines often patronizingly recommend what is considered acceptable or achievable, rather than what the best available balance of evidence suggests is best.

Why does the leading cancer and diet authority recommend we avoid bacon, ham, hot dogs, sausage, and all other processed meats—including chicken and turkey?

Potential culprits include the trans fat in meat, the saturated fat, cholesterol, heme iron, advanced glycation end products (glycotoxins), animal protein (especially leucine), zoonotic viruses, and industrial pollutants that accumulate up the food chain.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.

PBDE fire-retardant chemicals in the food supply may contribute to attention and cognitive deficits in children.

The FDA’s suggestion that the meat industry voluntarily stop feeding antibiotics by the ton to farm animals to fatten them faster falls short of the changes needed to forestall the epidemic of antibiotic resistance.
Studies on more than a thousand children suggest that a viral infection may play a role in childhood obesity by increasing both the number and size of fat cells.

Carcinogens in grilled and baked chicken may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, while curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, may sometimes help even in advanced stages of the disease.

By testing chicken feathers for chemical residues, researchers aim to find out what the poultry industry is feeding their birds. The presence of banned drugs and a broad range of pharmaceuticals raises concern, recalling the time in which DES was fed to chickens for years after it was shown to cause human vagina cancer.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting-edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our leading causes of death and disability.

Neurotoxins in chicken, such as the beta-carboline alkaloid harman, may explain the link between meat consumption and hand tremor, the most common movement disorder.

Does cooking meals at home lead to improved health outcomes? And how do TV dinners compare nutritionally to TV-chef recipes?

Though the most concentrated sources of the toxic metal cadmium are cigarette smoke, seafood, and organ meats, does greater consumption from whole grains and vegetables present a concern?
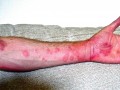
The rising incidence of tick-bite induced meat allergies may account for cases of previously unexplained (“idiopathic”) persistent hives among children.

The association between cancer and the consumption of deep-fried foods may be due to carcinogens formed at high temperatures in animal foods (heterocyclic amines and polycyclic hydrocarbons) and plant foods (acrylamide).

What if billions in tax dollars were invested in healthier options, rather than given to corporations to subsidize the very foods that are making us sick?
Arsenic-containing drugs intentionally added to poultry feed to reduce the parasite burden and pinken the meat are apparently converted by cooking into carcinogenic inorganic arsenic compounds.

The levels of arsenic, banned pesticides, and dioxins exceeded cancer benchmarks in each of the 364 children tested. Which foods were the primary sources of toxic pollutants for preschoolers and their parents?

The lifespan extension associated with dietary restriction may be due less to a reduction in calories, and more to a reduction in animal protein (particularly the amino acid leucine, which may accelerate aging via the enzyme TOR).

Phytic acid (phytate), concentrated in food such as beans, whole grains, and nuts, may help explain lower cancer rates among plant-based populations.

Foods of animal origin (especially fish) appear to be the most important source of human exposure to industrial pollutants such as alkylphenol xenoestrogens.

Used in about eight million pounds of meat every year in the United States, the “meat glue” enzyme, transglutaminase, has potential food safety and allergy implications.

Different brands of liquid smoke flavorings have been tested for DNA-damaging potential, p53 activation, and levels of known carcinogens. Smoked foods such as ham, turkey, barbequed chicken, herring, and salmon were also tested.

The oxidation of high-fat and cholesterol-rich foods in our stomachs may help explain why eating antioxidant packed foods appears to reduce heart attack and stroke risk.

Freedom of Information Act documents reveal that the U.S. Department of Agriculture warned the egg industry that saying eggs are nutritious or safe may violate rules against false and misleading advertising.

The meat industry sued the federal government, winning the right to sell food known to be contaminated with food-poisoning bacteria.

Foster Farms chicken may have infected and sickened more than 10,000 people, due to contamination of the meat with fecal material.
Organic produce may present less of a food safety risk, given the potential contamination of pesticides with fecal pathogens.
The level of multidrug antibiotic-resistant bacteria contamination is compared between meat from animals raised conventionally, and certified organic meat from animals raised without being fed antibiotics.

Eating meat or eggs before pregnancy may increase the risk of gestational diabetes.
Even nine servings of fruits and vegetables a day may not reach the minimum recommended intake of antioxidants if one doesn’t make the right choices.

The vast majority of chicken and poultry products are injected with phosphorus preservatives, which are often not listed in the ingredients. Reducing one’s intake of meat, junk food, fast food, and processed cheese may help lower intake until labeling is mandated.

The phosphorus preservatives injected into poultry may not just be an arterial toxin. They also appear to dramatically increase the growth of food poisoning Campylobacter bacteria.

The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.

Phytonutrients in certain plant foods may block the toxic effects of industrial pollutants, like dioxins, through the Ah receptor system.