
Pros and Cons of Raw Food Diets
Is there an advantage to eating a raw plant-based diet over a diet of raw and cooked whole plant foods?
Diets rich in carotenoids like beta-carotene may protect against radiation-induced DNA damage and oxidative stress in the lungs. Subjects suffering from asthma had lower circulating carotenoid levels; adding a few servings of fruits and vegetables to the diet reduced asthma exacerbation rate by half. Antioxidants like beta-carotene and vitamin C taken from diet could also help prevent bacterial vaginosis.
Plant-based foods contain more than 100,000 biologically active components—more specifically, more than 100,000 phyto-nutrients, phyto for the Greek word for plant. Blueberries have anthocyanins that may help with memory. Tomatoes are rich in the red pigment lycopene, which may help target heart disease and cancer, and ginger has gingerols that may help with hypertension. The list goes on. And we can’t just take these phytonutrients in a pill. When it comes to food, the whole is often greater than the sum of its parts. Beta carotene pills, for example, may actually increase cancer risk, as opposed to eating the whole carrot, including its carotenoid antioxidants, which may lower our risk.
So we should focus on dietary intake, not supplementary intake. Apparently, antioxidant supplements just do not have the same cancer-fighting effects as produce, and colorful foods are often healthier because of their antioxidant pigments, whether it’s the beta-carotene that makes carrots and sweet potatoes orange, the lycopene antioxidant pigment that makes tomatoes red, or the anthocyanin pigments that make blueberries blue. The colors are the antioxidants. That knowledge alone should revolutionize your stroll down the produce aisle.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Unsplash. This image has been modified.

Is there an advantage to eating a raw plant-based diet over a diet of raw and cooked whole plant foods?

Which might actually make cognition worse: Centrum multivitamin, vitamin C, beta carotene, Souvenaid, zinc, or calcium supplements?

Which foods can increase collagen deposition and prevent wrinkles?

What is the best way to get the nutrients of concern on a plant-based diet?

Foods that reduce inflammation. What does an anti-inflammatory diet look like?

How Dr. Greger pressure steams his greens.

Dark green leafy vegetables are the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. What’s the best way to prepare them?

Avocados, greens, and lutein and zeaxanthin supplements are put to the test for improving cognitive function.

What is the best source of lutein, the primary carotenoid antioxidant in the brain?

Is there any benefit to resveratrol? If so, should we get it from wine, grapes, peanuts, or supplements?

What role does diet and baby powder play in the development of fibroids and ovarian cancer?

What happened when cancer patients were given three quarters of a cup of canned tomato sauce every day for three weeks?

High doses of lycopene—the red pigment in tomatoes—were put to the test to see if it could prevent precancerous prostate lesions from turning into full-blown cancer.

What happened when turmeric curcumin was put to the test to see if it could reverse DNA damage caused by arsenic exposure?

Five cents’ worth of seaweed a day may dramatically improve a major cause of disability and compromised quality of life among women.

Combining certain foods together may be more beneficial than eating them separately.

Perhaps dietary guidelines should stress fresh, frozen, and dried fruit—rather than canned.
Those with higher vitamin D levels tend to have lower rates of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, but is it cause and effect? Interventional trials finally put vitamin D to the test.

Dietary diversity is important because each plant family has a unique combination of phytonutrients that may bind to specific proteins within our body.

The whole food is greater than the sum of its parts: how unscrupulous marketers use evidence that ties high blood levels of phytonutrients with superior health to sell dietary supplements that may do more harm than good.

Smoothies (and blended soups and sauces) offer a convenient way to boost both the quantity and quality of fruit and vegetable intake by reducing food particle size to help maximize nutrient absorption.

How does sweet potato baking compare to boiling and steaming, and should we eat the skin?

What role might the spice turmeric play in both the prevention of precancerous polyps, and the treatment of colorectal cancer?

Increasing fruit and vegetable consumption to seven servings a day appears to cut asthma exacerbation rates in half, whereas restricting consumption to Standard American Diet levels leads to a significant worsening of lung function and asthma control.

Based on studies of atomic bomb survivors, Chernobyl victims, and airline pilots exposed to more cosmic rays at high altitudes, it appears that fruits and vegetables may decrease radiation-induced chromosome damage.
A more plant-based diet may help prevent vaginal infections, one of the most common gynecological problems of young women.
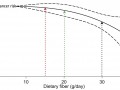
Inadequate fiber intake appears to be a risk factor for breast cancer, which can explain why women eating plant-based diets may be at lower risk.

People taking dietary supplements may, in some cases, be paying to make themselves sick. This video covers folic acid, beta carotene, and green tea supplements.

The accuracy of medical advice given by staff at natural food stores is compared to that given by staff at community pharmacies, based on the balance of available scientific evidence.

The risk of glaucoma, the second leading cause of blindness, appears to be dramatically reduced by kale or collard greens consumption, thanks to the phytonutrient pigments lutein and zeaxanthin.

The variety of fruit and vegetable consumption may decrease disease risk, independent of quantity.

Beeturia, the passage of pink urine after beetroot consumption, is a reminder that phytonutrients circulate throughout our bloodstream—explaining the connection between “garlic breath,” and the use of garlic as an adjunct treatment for pneumonia.

The Institute of Medicine’s conservative position on vitamin D is understandable, given the history of hyped vitamin supplements (vitamin A, beta carotene, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E) that turned out worthless—or worse.

Kale works better at boosting antioxidant levels in the skin than synthetic beta carotene, lutein, and mixed carotenoid supplements.