
Do the Health Impacts of Ultra-Processed Foods Apply to Plant-Based Meat Alternatives?
If the only ultra-processed food that appears to be killing people is meat, then plant-based meats may be the solution to the ultra-processed foods problem.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Linda
Soda consists mostly of empty sugar calories. One can of soda exceeds the American Heart Association’s recommended daily limit for sugar. Soda was ranked lowest among all beverage categories for health and nutritional value. Sugar in liquid form, such as soda, is particularly unhealthy, because our bodies do not seem to recognize the calories as much as when they are in solid form; this can lead to overeating. Sugar can also impair arterial function. Evidence from PET scans suggests brain activity changes from the overconsumption of sugar may parallel that of drug addiction.
Diet soda and the aspartame that sweetens it bring a different array of risks. The disconnect between sweetness sensations on the tongue and the lack of a caloric feedback loop in the gut may result in overeating. People consuming low or no-calorie sweeteners may eat more than they otherwise would because they believe they have saved enough calories to justify additional food intake. Frequent intake of diet drinks may increase depression risk among older adults; individuals with mood disorders appear particularly vulnerable to adverse effects of aspartame. Aspartame may be the reason that diet soda consumption during pregnancy has been linked to premature birth. One study has reported a link between diet soda and multiple myeloma, likely because of aspartame. Diet coke has more potential than any other tested food to cause erosion of tooth enamel.
Cola appears to raise cholesterol levels, and Coca-Cola has been found to be very low in antioxidants. The caramel coloring used in many sodas has been linked to cancer, a finding which has led to changes in soft drink formulation in California. Colas also contain phosphate additives, which appear to damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis. Gum arabic, found in some sodas, is harmless, but sodium benzoate, also found in some sodas, is harmful. And high fructose corn syrup may be contaminated with mercury.
Studies funded by the soda (and dairy) industry appear to be even more biased than studies funded by drug companies (and can include questionable alliances between major soda companies and organizations whose mission is to promote health). Industry influence is likewise seen in the USDA Dietary Guidelines, which did not go as far as those in other countries to advise against soft drink consumption.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Blake Wisz / Upsplash. This image has been modified.

If the only ultra-processed food that appears to be killing people is meat, then plant-based meats may be the solution to the ultra-processed foods problem.

Only two categories of ultra-processed foods have been associated with premature death.

Are there aspects of ultra-processed foods beyond their nutrient profile that contribute to their deleterious effects?

How many lives would be saved if everyone ate vegetarian or vegan?

Certain soft drinks and bottled (heated) carrot juice may contain carcinogenic levels above safety standards.

When we get dehydrated, the shrinkage of our blood volume can lead to the release of angiotensin, which can lead to weight gain.

Those who stay hydrated tend to maintain a healthier body weight, but is it cause and effect?

Not all plant foods are linked to less cellular aging based on telomere attrition, and not all animal foods are linked to more.

What kind of diet should cancer patients eat?

How can mandating healthy eating messaging on fast-food ads ironically make things worse?

How was England able to so successfully lower sodium intake, which was accompanied by dramatic drops in stroke and heart disease deaths?

The same person paid by Big Sugar to downplay the risks of sugar was paid by Big Meat to downplay the risks of meat.

The meat industry comes up with a perversion of evidence-based medicine.

How legitimate is the common corporate criticism of the scientific nutrition literature that the credibility of observational studies is questionable?

International Life Sciences Organization, a nonprofit, is accused of being a front group for Coca-Cola and other junk food giants.

A staggering 99.99 percent of Americans fail to get the minimum recommended potassium intake (despite it being perhaps only half of our natural intake) and stay below the recommended sodium intake (even though it may be twice our natural intake).

What happened when ultra-processed foods were matched for calories, sugar, fat, and fiber content in the first randomized controlled trial?

How did the meat industry, government, and cancer organizations respond to the confirmation that processed meat, like bacon, ham, hot dogs, and lunch meat, causes cancer?

Does the link between white potatoes and diabetes extend to non-fried potatoes without butter or sour cream?

The foundation of cancer prevention is plants, not pills.

Big Food uses our hard-wired drive for dietary diversity against us.

The leading risk factor for death in the United States is the American diet.

What are the three sources of the liver fat in fatty liver disease and how do you get rid of it?

What do hospitals have to say for themselves for feeding people meals that appear to be designed to inspire repeat business?
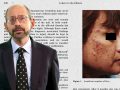
Acne can be triggered in one in ten people who get vitamin B12 injections.

Why is hospital food so unhealthy?

Two cups of cold water on an empty stomach a few times a day for weight loss.

The first study in history on the incidence of stroke of vegetarians and vegans suggests they may be at higher risk.

What is the relationship between stroke risk and dairy, eggs, meat, and soda?

We all like to think we make important life decisions like what to eat consciously and rationally, but if that were the case we wouldn’t be in the midst of an obesity epidemic.

The unprecedented rise in the power, scope, and sophistication of food marketing starting around 1980 aligns well with the blastoff slope of the obesity epidemic.

Why are U.S. taxpayers giving billions to support the likes of the sugar and livestock industries?

The common explanations for the cause of the obesity epidemic put forward by the food industry and policymakers, such as inactivity or a lack of willpower, are not only wrong, but actively harmful fallacies.

A review of reviews on the health effects of animal foods versus plant foods.

A review of reviews on the health effects of tea, coffee, milk, wine, and soda.

Given the power of chronotherapy—how the same dose of the same drugs taken at a different time of day can have such different effects—it’s no surprise that chronoprevention approaches, like meal timing, can also make a difference.

The industry’s response to the charge that breakfast cereals are too sugary.

The sugar industry’s response to evidence implicating sweeteners in the obesity epidemic.
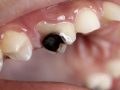
If sugar consumption is considered the one and only cause of cavities, how much is too much?

What about the recent studies that show cheese has neutral or positive health effects?