
How Much Water Should You Drink Every Day to Lose Weight?
When we get dehydrated, the shrinkage of our blood volume can lead to the release of angiotensin, which can lead to weight gain.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Randy
Active brown adipose tissue helps burn fat and raise metabolism; intake of arginine-rich foods (including soyfoods, seeds, nuts, and certain beans) as well as peppers with capsaicin can help activate that tissue. Eating plants may also help speed up metabolism due to greater insulin sensitivity in cells and the boosting of a key enzyme called Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase.
Nuts, green tea, and grape juice may particularly help raise metabolism, as can listening to music and exercise. How often we eat during the day apparently does not affect metabolism. A rare metabolic birth defect (1 in 40,000 people) can be resolved by carnitine supplements.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

When we get dehydrated, the shrinkage of our blood volume can lead to the release of angiotensin, which can lead to weight gain.

The SWAP-MEAT study puts Beyond Meat products to the test.

What did a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hibiscus tea for weight loss find?

Why can a single meal high in saturated fat impair cognition?

Fasting and exercise can boost the longevity hormone FGF21, but what can we eat—or avoid eating—to get similar effects?

What can we do to boost the longevity hormone FGF21?

Two cups of cold water on an empty stomach a few times a day for weight loss.

Drink two cups of water and you can get a surge of the adrenal hormone noradrenaline in your bloodstream, as if you just smoked a few cigarettes or downed a few cups of coffee.

The diving reflex shows that it’s possible to have selective adrenal hormone effects.

What shift workers can do to moderate the adverse effects of circadian rhythm disruption.

Bright light exposure synchronizes the central circadian clock in our brains, whereas proper meal timing helps sync the timing of the clock genes throughout the rest of our body.

The same meal eaten at the wrong time of day can double blood sugars.

Grape juice and whole grapes are put to the test for brain function, including cognitive decline in early Alzheimer’s.

A calorie is not a calorie—it not only depends on what you eat, but when you eat.

Breakthroughs in the field of chronobiology—the study of our circadian rhythms—help solve the mystery of the missing morning calories in breakfast studies.
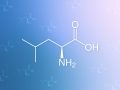
Why we may want to strive not to exceed the recommended intake of protein.

Calories eaten in the morning count less and are healthier than calories eaten in the evening.

Are there benefits to giving yourself a bigger daily break from eating?

17 ingredients to an ideal weight-loss diet and the 21 tweaks to accelerate the further loss of excess body fat.

The effects of eating only 5 days a week or a fasting-mimicking diet 5 days a month.

In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.

Alternate-day modified fasting is put to the test for lifespan extension.

Eating every other day can raise your cholesterol.
Does every-other-day-eating prevent the metabolic slowing that accompanies weight loss or improve compliance over constant day-to-day calorie restriction?

How to preserve bone and mass on a low calorie diet.

Though a bane for dieters, a slower metabolism may actually be a good thing.

Losing a pound of fat can take as few as 10 calories a day or as many as 55, depending on whether you’re improving food quality or just restricting food quantity.

Understanding the metabolic and behavioral adaptations that slow weight loss.

How many fewer calories do you have to eat every day to lose one pound of body fat?

The reason egg consumption is associated with elevated cancer risk may be the TMAO, considered the “smoking gun” of microbiome-disease interactions.
What’s more important: probiotics or prebiotics? And where can we best get them?

The reason greens are associated with a significantly longer lifespan may be because, like caloric restriction, they improve our energy efficiency.

The fat-burning properties of brown adipose tissue can be boosted by cold exposure, certain flavor molecules, and arginine-rich foods.

Brown adipose tissue is a unique organ that burns fat to create heat, improving temperature regulation in infants and weight loss in adults.

Music can beat out anti-anxiety drugs, Mozart can reduce allergic reactions, and how listening to your favorite tunes can significantly affect your testosterone levels.

Employee wellness programs may help boost the corporate bottom line.

What role has inactivity played in the obesity epidemic and how much should we be exercising?

Americans eating meat-free diets average higher intakes of nearly every nutrient, while maintaining a lower body weight—perhaps due, in part, to their higher resting metabolic rates.

Despite the caloric density of both nuts and dried fruit, they do not appear to lead to the expected weight gain.

A review of the best available science examining the impact of eating frequency on both weight and health.