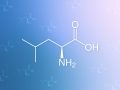
Are BCAA (Branched Chain Amino Acids) Healthy?
Why we may want to strive not to exceed the recommended intake of protein.

Why we may want to strive not to exceed the recommended intake of protein.

The effects of eating only 5 days a week or a fasting-mimicking diet 5 days a month.

In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.

How to preserve bone and mass on a low calorie diet.

I was honored to testify before the US government’s Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. Check out the video to see my speech and a few of my favorite excerpts.

Keto diets put to the test for diabetes reversal.

Ketogenic diets found to undermine exercise efforts and lead to muscle shrinkage and bone loss.

The effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk.

Might the appetite-suppressing effects of ketosis improve dietary compliance?

Ketogenic diets and the $33-billion diet gimmick.

Do low-carb and ketogenic diets have a metabolic advantage for weight loss?

The clinical use of ketogenic diets for epilepsy and cancer: what does the science say?

Are flax seeds like bitter almonds, where just a few ounces could kill you, or more like regular almonds, where regular dietary intake wouldn’t even come close?

How do we explain the increased risk of prostate cancer but the decreased risk of colon cancer associated with dairy consumption?

The relationship between the consumption of eggs and other cholesterol-rich foods and cancers of the colon, breast, endometrium, pancreas, and throat.

Dairy is compared to other foods for cardiovascular (heart attack and stroke) risk.

The secret to unlocking the benefits of chia seeds may be grinding them up.

What happened when researchers tried to tease out what’s in dairy that interferes with the health benefits of berries and tea?

High-fat plant foods—avocados, peanuts, and walnuts—and olive oil are put to the test.

Why are millions of dollars spent on shark cartilage supplements?

What are the effects of dairy products, sugar, and chocolate on the formation of pimples?

Does excluding dairy products, food additives, and gluten-containing grains from one’s diet help those with recurring canker sores (aphthous ulcers)?

What did the most comprehensive double-blind study of diet for autism find, and what are the potential downsides?

What happens when autistic children on gluten- and casein-free diets are covertly challenged with wheat and dairy?

The original randomized, controlled trials of gluten- and casein-free diets may have been complicated by parental expectation bias.

What were the results of the first randomized controlled study of a dietary intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?

The casomorphins—breakdown products of casein, a milk protein, with opiate-like activity—in bovine milk appear to have opposite effects than those from human breast milk on infant development, but what about A2 cow’s milk?

Casomorphins—breakdown products of casein, a milk protein, with opiate-like activity—may help explain why autism symptoms sometimes improve with a dairy-free diet.

Avocado consumption can improve artery function, but what effect might guacamole have on cancer risk?

Dramatic improvements in autistic children when they have a fever suggest that the disease may be reversible if one can replicate the phenomenon in other ways.

I recommend people switch away from using rice milk.

Whole plant sources of sugar and fat can ameliorate some of the postprandial (after-meal) inflammation caused by the consumption of refined carbohydrates and meat.

Within hours of eating an unhealthy meal, we can get a spike in inflammation, crippling our artery function, thickening our blood, and causing a fight-or-flight nerve response. Thankfully, there are foods we can eat at every meal to counter this reaction.

What effect do chia seeds have on weight loss, blood sugar, cholesterol, blood pressure, and inflammation?

The FDA appears to have caved to industry pressure and allows intestines potentially infected with mad cow disease prions into food products and lipstick.

The majority of specialists in the field agreed that paraTB in meat and dairy likely represents a risk to human health and should be a high- or medium-priority public health issue.

“Fear of consumer reaction” led the U.S. dairy industry to suppress the discovery in retail milk of live paraTB bacteria, a pathogen linked to type 1 diabetes.

What happened to women who were randomized to eat more meat and dairy during pregnancy? What effect does animal protein consumption have on cortisol and testosterone levels in men?

Is it the casein or the cow insulin that explains the link between milk consumption and the development of type I diabetes?

Why might exposure to bovine proteins increase the risk of childhood-onset autoimmune type 1 diabetes?