
Fasting for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Fasting, followed by a plant-based diet, is put to the test for autoimmune inflammatory joint disease.

Fasting, followed by a plant-based diet, is put to the test for autoimmune inflammatory joint disease.

The temporary quintupling of heart attack risk associated with cannabis smoking may be due to the increased heartrate, blood pressure, and carbon monoxide levels.

An entire issue of a cardiology journal dedicated to plant-based nutrition explores the role an evidence-based diet can play in the reversal of congestive heart failure.

Why is hospital food so unhealthy?

Why the current Recommended Daily Allowance for vitamin B12 may be insufficient.

Is it possible to reverse type 1 diabetes if caught early enough?

Those on a healthy plant-based diet with elevated homocysteine levels despite taking sufficient vitamin B12 may want to consider taking a gram a day of contaminant-free creatine.

What are the consequences of having to make your own creatine rather than relying on dietary sources?

Many doctors mistakenly rely on serum B12 levels in the blood to test for vitamin B12 deficiency.

Not taking B12 supplements or regularly eating B12 fortified foods may explain the higher stroke risk found among vegetarians.

Might animal protein-induced increases in the cancer-promoting grown hormone IGF-1 help promote brain artery integrity?

How can we explain the drop in stroke risk as the Japanese diet became Westernized by eating more meat and dairy?

Just because you’re eating vegetarian or vegan doesn’t mean you’re eating healthy.

Does eating fish or taking fish oil supplements reduce stroke risk?

Could the apparent increased stroke risk in vegetarians be reverse causation? And what about vegetarians versus vegans?

The first study in history on the incidence of stroke of vegetarians and vegans suggests they may be at higher risk.

What is the relationship between stroke risk and dairy, eggs, meat, and soda?

We need to reform the food system before it’s too late.

There are things you can do right now to reduce your risk of falling seriously ill and dying from this disease.

What to eat and what to avoid to lower the cardiovascular disease risk factor lipoprotein(a).

What is this lipoprotein(a) and what can we do about it?

A review of reviews on the health effects of animal foods versus plant foods.

How to treat the cause by preventing the emergence of pandemic viruses in the first place (a video I recorded more than a decade ago when I was Public Health Director at the HSUS in Washington DC).

A review of reviews on the health effects of tea, coffee, milk, wine, and soda.
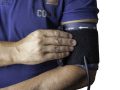
Natural approaches to lowering high blood pressure can work better than drugs because you’re treating the underlying cause, and can end up having only good side effects.

What shift workers can do to moderate the adverse effects of circadian rhythm disruption.

Ancient wheats like kamut are put to the test for inflammation, blood sugar, and cholesterol control.

The same meal eaten at the wrong time of day can double blood sugars.

Raw garlic is compared to roasted, stir-fried, simmered, and jarred garlic.

Given the power of chronotherapy—how the same dose of the same drugs taken at a different time of day can have such different effects—it’s no surprise that chronoprevention approaches, like meal timing, can also make a difference.

See what a penny a day worth of garlic powder can do.

Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory, aging-associated oxylipins can be normalized by eating ground flaxseed.

In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.

Eating every other day can raise your cholesterol.

Peeled apples are pitted head-to-head against unpeeled apples and spinach in a test of artery function.

Keto diets put to the test for diabetes reversal.

Ketogenic diets found to undermine exercise efforts and lead to muscle shrinkage and bone loss.

The effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk.

Why don’t more people take the weight loss medications currently on the market?

Plant-based diets as the single most important, yet underutilized, opportunity to reverse the pending obesity and diabetes-induced epidemic of disease and death.