
The Thrifty Gene Theory: Survival of the Fattest
Rather than being some kind of disorder or failure of willpower, weight gain is largely a normal response, by normal people, to an abnormal situation.

Rather than being some kind of disorder or failure of willpower, weight gain is largely a normal response, by normal people, to an abnormal situation.

The big fat “fat gene” accounts for less than 1% of the differences in size between people.

How to treat the cause by preventing the emergence of pandemic viruses in the first place (a video I recorded more than a decade ago when I was Public Health Director at the HSUS in Washington DC).

Healthier plant-based diets compared to unhealthy plant foods and animal foods on diabetes risk.

What shift workers can do to moderate the adverse effects of circadian rhythm disruption.

Ancient wheats like kamut are put to the test for inflammation, blood sugar, and cholesterol control.

The same meal eaten at the wrong time of day can double blood sugars.
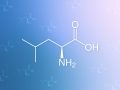
Why we may want to strive not to exceed the recommended intake of protein.

In this live presentation, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his book How Not to Diet.

Eating every other day can raise your cholesterol.

Understanding the metabolic and behavioral adaptations that slow weight loss.

Keto diets put to the test for diabetes reversal.

Plant-based diets as the single most important, yet underutilized, opportunity to reverse the pending obesity and diabetes-induced epidemic of disease and death.

Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials on berries and the first clinical study on the effects of berries on arthritis.

The case for using a plant-based diet to reduce the burden of diabetes has never been stronger.

Genetic differences in caffeine metabolism may explain the Jekyll and Hyde effects of coffee.

Blueberries are put to the test against insulin resistance, oxidation, and DNA damage.

Ground ginger and ginger tea are put to the test for blood sugar control.

Dark roast coffee is more effective than light roast coffee in reducing body weight.

Dairy is compared to other foods for cardiovascular (heart attack and stroke) risk.

Cocoa and nitrite-rich vegetables, such as green leafies and beets, are put to the test for cognitive function.

What happens when you add massive amounts of carbs to the daily diet of type 2 diabetics in the form of whole grains?

What happens when you put diabetics on a diet composed of largely whole grains, vegetables, and beans?

What is the return on investment for educating employees about healthy eating and living?

The most well-published community-based lifestyle intervention in the medical literature is also one of the most effective.

The CHIP program has attempted to take the pioneering lifestyle medicine work of Pritikin and Ornish and spread it into the community.
A half-teaspoon a day of brewer’s yeast is put to the test in a randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial.

Chicken, fish, and egg powder in processed foods present greater risk from cholesterol oxidation byproducts, but there are things you can do to reduce exposure.

What does a review of the evidence on the effects of coconut oil on weight loss and belly fat find?

Are the apparently amazing benefits of amla—dried Indian gooseberries—too good to be true?

What are the risks and benefits of getting an annual check-up from your doctor?

What happened when turmeric curcumin was put to the test to see if it could reverse DNA damage caused by arsenic exposure?

How can we properly cook beans?

A book purported to expose “hidden dangers” in healthy foods doesn’t even pass the whiff test.

Are there unique benefits to brown rice that would justify keeping it in our diet despite the arsenic content?

Do the health benefits of rice consumption outweigh any potential risk from the arsenic contamination?

A daily half-cup of cooked rice may carry a hundred times the acceptable cancer risk of arsenic. What about seaweed from the coast of Maine?

Even at low-level exposure, arsenic is not just a class I carcinogen, but may also impair our immune function and increase our risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
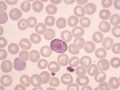
Since white blood cell count is a sign of systemic inflammation, it’s no surprise that those with lower white blood cell counts live longer.

Physical fitness authorities seem to have fallen into the same trap as the nutrition authorities, recommending what they think may be achievable, rather than simply informing us what the science says and letting us make up our own mind.